OOPS/C#
Interview question
https://www.wisdomjobs.com/e-university/advanced-c-hash-interview-questions.html
https://www.guru99.com/c-sharp-interview-questions.html
https://www.guru99.com/c-sharp-interview-questions.html
Best concepts c#
https://www.completecsharptutorial.com/basic/referencetype-parameter.php
Difference between Abstract Class and Interface
| ABSTRACT CLASS | INTERFACE |
|---|---|
| It contains both declaration and definition part. | It contains only a declaration part. |
| Multiple inheritance is not achieved by abstract class. | Multiple inheritance is achieved by interface. |
| It contain constructor. | It does not contain constructor. |
| It can contain static members. | It does not contain static members. |
| It can contain different types of access modifiers like public, private, protected etc. | It only contains public access modifier because everything in the interface is public. |
| The performance of an abstract class is fast. | The performance of interface is slow because it requires time to search actual method in the corresponding class. |
| It is used to implement the core identity of class. | It is used to implement peripheral abilities of class. |
| A class can only use one abstract class. | A class can use multiple interface. |
| If many implementations are of the same kind and use common behavior, then it is superior to use abstract class. | If many implementations only share methods, then it is superior to use Interface. |
| Abstract class can contain methods, fields, constants, etc. | Interface can only contain methods . |
| It can be fully, partially or not implemented. | It should be full |
- An Abstract class doesn't provide full abstraction but an interface does provide full abstraction; i.e. both a declaration and a definition is given in an abstract class but not so in an interface.
- Using Abstract we cannot achieve multiple inheritance but using an Interface we can achieve multiple inheritance.
- We can not declare a member field in an Interface.
- We can not use any access modifier i.e. public, private, protected, internal etc. because within an interface by default everything is public.
- An Interface member cannot be defined using the keyword static, virtual, abstract or sealed.
Access Modifiers :
public: Access is not restricted.protected: Access is limited to the containing class or types derived from the containing class.internal: Access is limited to the current assembly.protected internal: Access is limited to the current assembly or types derived from the containing class.private: Access is limited to the containing type.private protected: Access is limited to the containing class or types derived from the containing class within the current assembly.
| Default | Permitted declared accessibilities
------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace | public | none (always implicitly public)
enum | public | none (always implicitly public)
interface | internal | public, internal
class | internal | public, internal
struct | internal | public, internal
delegate | internal | public, internalfunction/members | privateC# Static Constructor
A static or non-static class can have a static constructor without any access modifiers like public, private, protected, etc.
A static constructor in a non-static class runs only once when the class is instantiated for the first time.
A static constructor in a static class runs only once when any of its static members accessed for the first time.
C#, Private Constructor :
C#, Private Constructor :
Private Constructor is a special instance constructor and
it is used in a classes that contains only static members.
If a class contains one or more private constructors and no public constructors,
then the other classes are not allowed to create an instance for that particular
class except nested classes.
it is used in a classes that contains only static members.
If a class contains one or more private constructors and no public constructors,
then the other classes are not allowed to create an instance for that particular
class except nested classes.
Use Keyword as Identifier
Prefix '@' with keywords if you want to use it as identifier.
public class @class
{
public static int MyProperty { get; set; }
}
@class.MyProperty = 100;Anonymous Type
Anonymous type, as the name suggests, is a type that doesn't have any name. C# allows you to create an object with the new keyword without defining its class. The implicitly typed variable- var is used to hold the reference of anonymous types.
var myAnonymousType = new { firstProperty = "First", secondProperty = 2,
thirdProperty = true }
1. Anonymous type can be defined using the new keyword and object
initializer syntax.
2. The implicitly typed variable-var, is used to hold an anonymous type.
3. Anonymous type is a reference type and all the properties are read-only.
4. The scope of an anonymous type is local to the method where it is defined.
5.You can pass it to a method that accepts a parameter of dynamic type .
Ref: http://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-anonymous-type
Dynamic Type :
-
The dynamic types are resolved at runtime instead of compile time.
-
The compiler skips the type checking for dynamic type. So it doesn't
give any error about dynamic types at compile time.
-
The dynamic types do not have intellisense support in visual studio.
-
A method can have parameters of the dynamic type.
-
An exception is thrown at runtime if a method or property is not
compatible.
Indexer
An Indexer is a special type of property that allows a class or structure to
be accessed the same way as array for its internal collection. It is same as
property except that it defined with this keyword with square bracket
and parameters.
- 1. An indexer is same as property except that it defined with this keyword with square bracket that takes paramter.
- 2. Indexer can be override by having different types of parameters.
- 3. Ref and out parameter with the indexer is not supported.
- 4. Indexer can be included as an interface member.
Public <return type> this[<parameter type> index]
{
Get{
// return the value from the specified index
}
Set{
// set values at the specified index
}
}
Params :
By using the params keyword, you can specify a method parameter that takes
a variable number of arguments.
You can send a comma-separated list of arguments of the type specified in the
parameter declaration or an array of arguments of the specified type. You also
can send no arguments. If you send no arguments, the length of the params
list is zero.No additional parameters are permitted after the params keyword
in a method declaration, and only one params keyword is permitted in a
method declaration.
Tuple :
A tuple is a data structure that contains a sequence of elements of different data types. It can be used where you want to have a data structure to hold an object with properties, but you don't want to create a separate type for it.
Tuple<int, string, string> person =
new Tuple <int, string, string>(1, "Steve", "Jobs");
var person = Tuple.Create(1, "Steve", "Jobs");
person.Item1; // returns 1
person.Item2; // returns "Steve"
- Tuple is a reference type and not a value type. It allocates on heap and could result in CPU intensive operations.
- Tuple is limited to include 8 elements. You need to use nested tuples if you need to store more elements. However, this may result in ambiguity.
- Tuple elements can be accessed using properties with a name pattern Item<elementNumber> which does not make sense.
- When you want to return multiple values from a method without using
ref or outparameters.
- When you want to pass multiple values to a method through a single parameter.
- When you want to hold a database record or some values temporarily without creating a separate class.
C# Collection:
There are two types of collections available in C#: non-generic collections and generic collections.
Non-generic collections:
The System.Collections namespace includes the interfaces and classes for the non-generic collections.
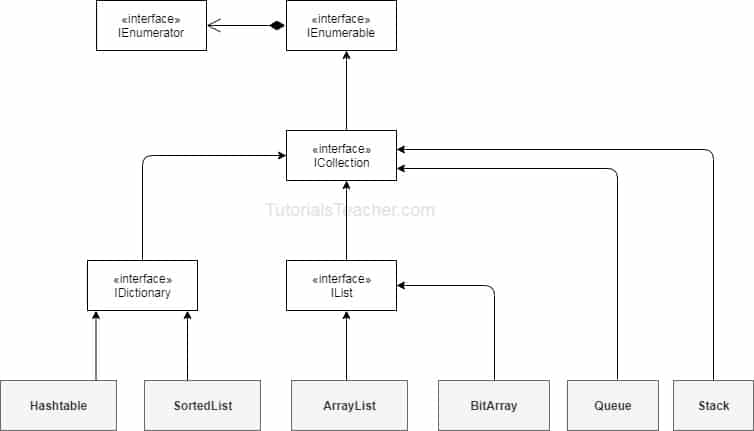 Reference : http://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-collection
Reference : http://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-collection
Generic Collection :
The limitation of Non-generic collections is that while retrieving items, you need to cast into the appropriate data type, otherwise the program will throw a runtime exception. It also affects on performance, because of boxing and unboxing.
To overcome this problem, C# includes generic collection classes in the System.Collections.Generic namespace.
doesn't need to do boxing and unboxing.
List<T>:contains elements of specified type.
It grows automatically as you add elements in it.
Dictionary<TKey,TValue> contains key-value pairs.
SortedList<TKey,TValue> stores key and value pairs.
It automatically adds the elements in ascending order of key by default.
Hashset<T> contains non-duplicate elements. It eliminates duplicate elements.
Queue<T> stores the values in FIFO style (First In First Out).
Stack<T> stores the values as LIFO (Last In First Out).
- List<T> stores elements of the specified type and it grows automatically.
- List<T> can store multiple null and duplicate elements.
- List<T> can be assigned to IList<T> or List<T> type of variable. It provides more helper method When assigned to List<T> variable
- List<T> can be access using indexer, for loop or foreach statement.
- LINQ can be use to query List<T> collection.
- List<T> is ideal for storing and retrieving large number of elements.
C# - Dictionary<TKey, TValue>
System.Collection.Generics namespaceDictionary cannot include duplicate or null keys,where as values can be duplicated or set as null.IDictionary<int, string> dict = new Dictionary<int, string>(); //or Dictionary<int, string> dict = new Dictionary<int, string>();
- A Dictionary stores Key-Value pairs where the key must be unique.
- Before adding a KeyValuePair into a dictionary, check that the key does not exist using the ContainsKey() method.
- Use the TryGetValue() method to get the value of a key to avoid possible runtime exceptions.
- Use a foreach or for loop to iterate a dictionary.
- Use dictionary indexer to access individual item.
- Use custom class that derives IEqualityComparer to compare object of custom class with Contains() method.
- Reference :http://www.tutorialsteacher.com/csharp/csharp-dictionary
C# - SortedList<TKey, TValue>
- C# has a generic and non-generic SortedList.
- SortedList stores the key-value pairs in ascending order of the key. The key must be unique and cannot be null whereas value can be null or duplicate.
- Generic SortedList stores keys and values of specified data types. So no need for casting.
- Key-value pair can be cast to a KeyValuePair<TKey,TValue>.
- An individual value can be accessed using an indexer. SortedList indexer accepts key to return value associated with it.
Exception in C#
An application may encounter an error during the execution. When an error occurs, either CLR or program code throws an exception which contains necessary information about the error. There are two types of exceptions in .Net, exceptions generated by the executing program and exceptions generated by the CLR.
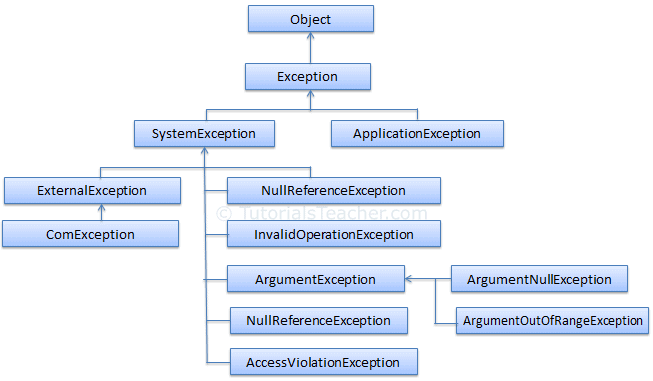
- Exception is a base class for any type of exception class in C#.
- Exception types: SystemException and ApplicationException.
- SystemException class is used for CLR related runtime errors.
- Exception class includes important properties e.g Message, StackTrack, InnerException, data etc. to associate important information with every exception.
- Use the try, catch and finally blocks to handle exceptions in C#.
- The try block must be followed by a catch or finally block or both.
- A multiple catch block is allowed with different exception filters. General catch{..} block must come last.
catch{..} and catch(Exception ex){ } both cannot be used.- The finally block must come after the try or catch block.
- The finally block will always execute irrespective of whether an exception occured or not.
- The finally block is appropriate place for disposing objects.
- The finally block cannot have a return or break because it isn't allow to leave the control.
- Nested try-catch blocks are allowed in C#.
- An Exception will be catched in the inner catch block if appropriate filter found, otherwise will be catched by outer catch block.
Throw:
An exception can be raised manually by using the throw keyword.
Any type of exceptions which is derived from Exception class
can be raised using the throw keyword.
C# - Delegate :
A delegate is like a pointer to a function. It is a reference type data type and it holds the reference of a method. All the delegates are implicitly derived from System.Delegateclass.
public delegate void Print(int value);
- Delegate is a function pointer. It is reference type data type.
- Syntax: public delegate void <function name>(<parameters>)
- A method that is going to assign to delegate must have same signature as delegate.
- Delegates can be invoke like a normal function or Invoke() method.
- Multiple methods can be assigned to the delegate using "+" operator. It is called multicast delegate.
C# - Anonymous Method:
an anonymous method is a method without a name. Anonymous methods in C# can be defined using the delegate keyword and can be assigned to a variable of delegate type.
public delegate void Print(int value);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Print print = delegate(int val) {
Console.WriteLine("Inside Anonymous method. Value: {0}", val);
};
print(100);
}
- Anonymous method can be defined using the delegate keyword
- Anonymous method must be assigned to a delegate.
- Anonymous method can access outer variables or functions.
- Anonymous method can be passed as a parameter.
- Anonymous method can be used as event handlers.
- It cannot access ref or out parameter of an outer method.
Nullable Type in C#:
Nullable types that allow you to assign null to value type variables.
- You can only use == and != operators with a nullable type. For other comparison use the Nullable static class.
?? Operator :
Use the '??' operator to assign a nullable type to anon-nullable type.
int? i = null;
int j = i ?? 0;
C# - Predicate Delegate :
It represents a method that contains a set of criteria and
checks whether the passed parameter meets those criteria or not.
A predicate delegate methods must take one input parameter and
return a boolean - true or false.
Predicate<string> isUpper = delegate(string s)
{ return s.Equals(s.ToUpper());};
bool result = isUpper("hello world!!");
- Anonymous method and Lambda expression can be assigned to the predicate delegate.
C# - Extension Method :
Extension methods allow you to inject additional methods without modifying,
framework classes, or third party classes or interfaces.
Extension methods can be added to your own custom class, .NET
deriving or recompiling the original class, struct or interface.
- The first parameter of the extension method must be of the type for which the extension method is applibable, preceded by the this keyword.
- Extension methods can be used anywhere in the application by including the namespace of the extension method.
- Define a static method as an extension method where the first parameter of the extension method specifies the type on which the extension method is applicable.
C# - Object Initializer:
Object initializers allow you to assign values to the fields or properties at
the time of creating an object without invoking a constructor.
var student1 = new Student() { StudentID = 1, StudentName = "John" };
More...C# Interview Questions
ReplyDelete